笔记本API
Notebook API 允许 Visual Studio Code 扩展将文件作为笔记本打开、执行笔记本代码单元以及以各种丰富的交互式格式呈现笔记本输出。您可能知道流行的笔记本界面,例如 Jupyter Notebook 或 Google Colab - Notebook API 允许在 Visual Studio Code 中提供类似的体验。
笔记本的部件
笔记本由一系列单元及其输出组成。笔记本的单元格可以是Markdown 单元格或代码单元格,并在 VS Code 的核心内呈现。输出可以是多种格式。某些输出格式(例如纯文本、JSON、图像和 HTML)由 VS Code 核心呈现。其他的,例如特定于应用程序的数据或交互式小程序,由扩展呈现。
笔记本中的单元格由 读取和写入文件系统NotebookSerializer,它处理从文件系统读取数据并将其转换为单元格的描述,以及将对笔记本的修改持久保存回文件系统。笔记本的代码单元可以由 执行,它NotebookController获取单元的内容并从中生成零个或多个各种格式的输出,从纯文本到格式化文档或交互式小程序。应用程序特定的输出格式和交互式小程序输出由NotebookRenderer.
视觉上:
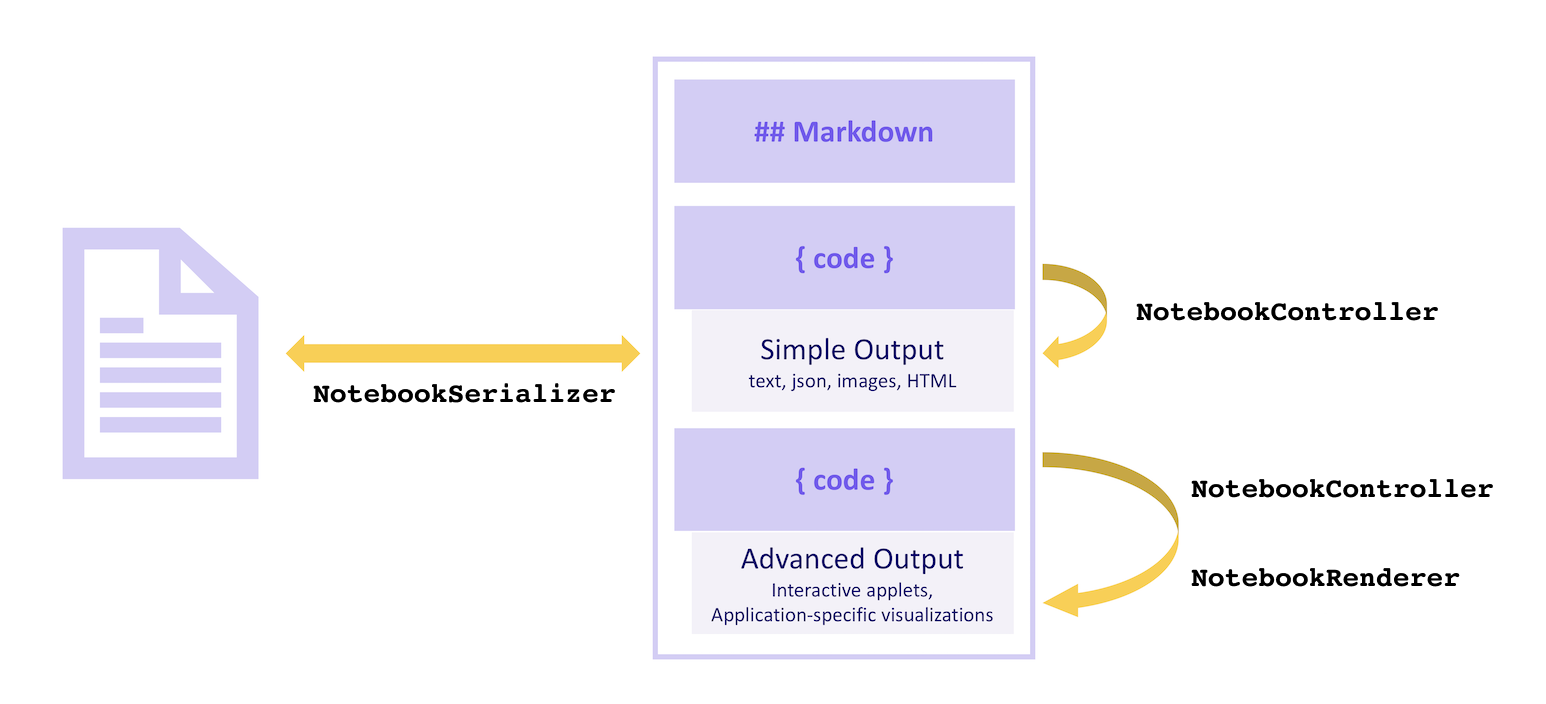
串行器
ANotebookSerializer负责获取笔记本的序列化字节并将这些字节反序列化为NotebookData,其中包含 Markdown 和代码单元的列表。它还负责相反的转换:获取NotebookData数据并将其转换为要保存的序列化字节。
样品:
- JSON Notebook Serializer:简单的示例笔记本,它采用 JSON 输入并在自定义 .json 文件中输出经过美化的 JSON
NotebookRenderer。 - Markdown Serializer:作为笔记本打开和编辑 Markdown 文件。
例子
在此示例中,我们构建了一个简化的笔记本提供程序扩展,用于查看带有扩展名(而不是传统文件扩展名)的Jupyter Notebook 格式的文件。.notebook.ipynb
package.json笔记本序列化器在该部分下声明contributes.notebooks如下:
{
...
"contributes": {
...
"notebooks": [
{
"type": "my-notebook",
"displayName": "My Notebook",
"selector": [
{
"filenamePattern": "*.notebook"
}
]
}
]
}
}
然后,笔记本序列化程序在扩展的激活事件中注册:
import { TextDecoder, TextEncoder } from 'util';
import * as vscode from 'vscode';
export function activate(context: vscode.ExtensionContext) {
context.subscriptions.push(
vscode.workspace.registerNotebookSerializer('my-notebook', new SampleSerializer())
);
}
interface RawNotebook {
cells: RawNotebookCell[];
}
interface RawNotebookCell {
source: string[];
cell_type: 'code' | 'markdown';
}
class SampleSerializer implements vscode.NotebookSerializer {
async deserializeNotebook(
content: Uint8Array,
_token: vscode.CancellationToken
): Promise<vscode.NotebookData> {
var contents = new TextDecoder().decode(content);
let raw: RawNotebookCell[];
try {
raw = (<RawNotebook>JSON.parse(contents)).cells;
} catch {
raw = [];
}
const cells = raw.map(
item =>
new vscode.NotebookCellData(
item.cell_type === 'code'
? vscode.NotebookCellKind.Code
: vscode.NotebookCellKind.Markup,
item.source.join('\n'),
item.cell_type === 'code' ? 'python' : 'markdown'
)
);
return new vscode.NotebookData(cells);
}
async serializeNotebook(
data: vscode.NotebookData,
_token: vscode.CancellationToken
): Promise<Uint8Array> {
let contents: RawNotebookCell[] = [];
for (const cell of data.cells) {
contents.push({
cell_type: cell.kind === vscode.NotebookCellKind.Code ? 'code' : 'markdown',
source: cell.value.split(/\r?\n/g)
});
}
return new TextEncoder().encode(JSON.stringify(contents));
}
}
现在尝试运行您的扩展并打开使用该.notebook扩展保存的 Jupyter Notebook 格式的文件:
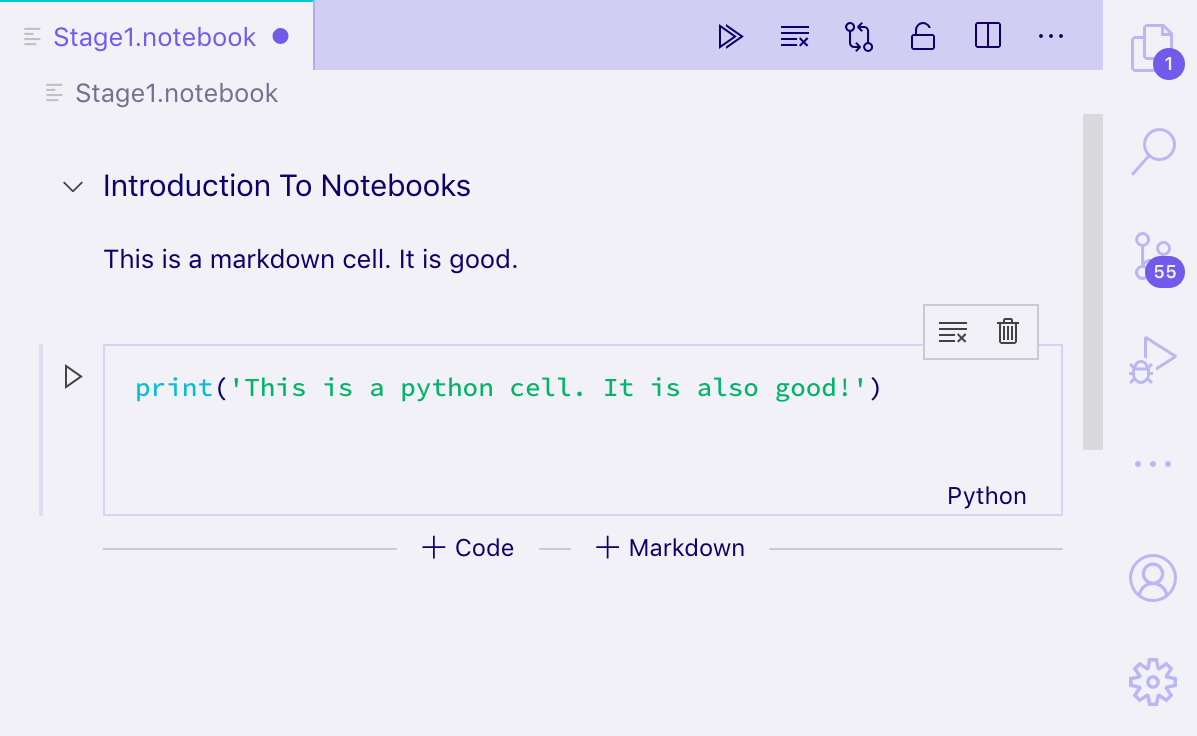
您应该能够打开 Jupyter 格式的笔记本并以纯文本和渲染的 Markdown 形式查看其单元格,以及编辑单元格。但是,输出不会持久保存到磁盘;要保存输出,您还需要序列化和反序列化来自 的单元格的输出NotebookData。
要运行单元,您需要实现一个NotebookController.
控制器
ANotebookController负责获取代码单元并执行代码以产生一些输出或不产生输出。
NotebookController#notebookType通过在创建控制器时设置属性,控制器直接与笔记本序列化器和笔记本类型相关联。然后,通过在激活扩展时将控制器推送到扩展订阅上来全局注册控制器。
export function activate(context: vscode.ExtensionContext) {
context.subscriptions.push(new Controller());
}
class Controller {
readonly controllerId = 'my-notebook-controller-id';
readonly notebookType = 'my-notebook';
readonly label = 'My Notebook';
readonly supportedLanguages = ['python'];
private readonly _controller: vscode.NotebookController;
private _executionOrder = 0;
constructor() {
this._controller = vscode.notebooks.createNotebookController(
this.controllerId,
this.notebookType,
this.label
);
this._controller.supportedLanguages = this.supportedLanguages;
this._controller.supportsExecutionOrder = true;
this._controller.executeHandler = this._execute.bind(this);
}
private _execute(
cells: vscode.NotebookCell[],
_notebook: vscode.NotebookDocument,
_controller: vscode.NotebookController
): void {
for (let cell of cells) {
this._doExecution(cell);
}
}
private async _doExecution(cell: vscode.NotebookCell): Promise<void> {
const execution = this._controller.createNotebookCellExecution(cell);
execution.executionOrder = ++this._executionOrder;
execution.start(Date.now()); // Keep track of elapsed time to execute cell.
/* Do some execution here; not implemented */
execution.replaceOutput([
new vscode.NotebookCellOutput([
vscode.NotebookCellOutputItem.text('Dummy output text!')
])
]);
execution.end(true, Date.now());
}
}
如果您要NotebookController与其序列化程序分开发布 -providing 扩展,请notebookKernel<ViewTypeUpperCamelCased>在keywords其package.json. 例如,如果您发布了github-issues笔记本类型的替代内核,则应该notebookKernelGithubIssues向您的扩展添加关键字关键字。
样品:
- GitHub Issues Notebook:执行 GitHub Issues 查询的控制器
- REST Book:运行 REST 查询的控制器。
- Regexper 笔记本:可视化正则表达式的控制器。
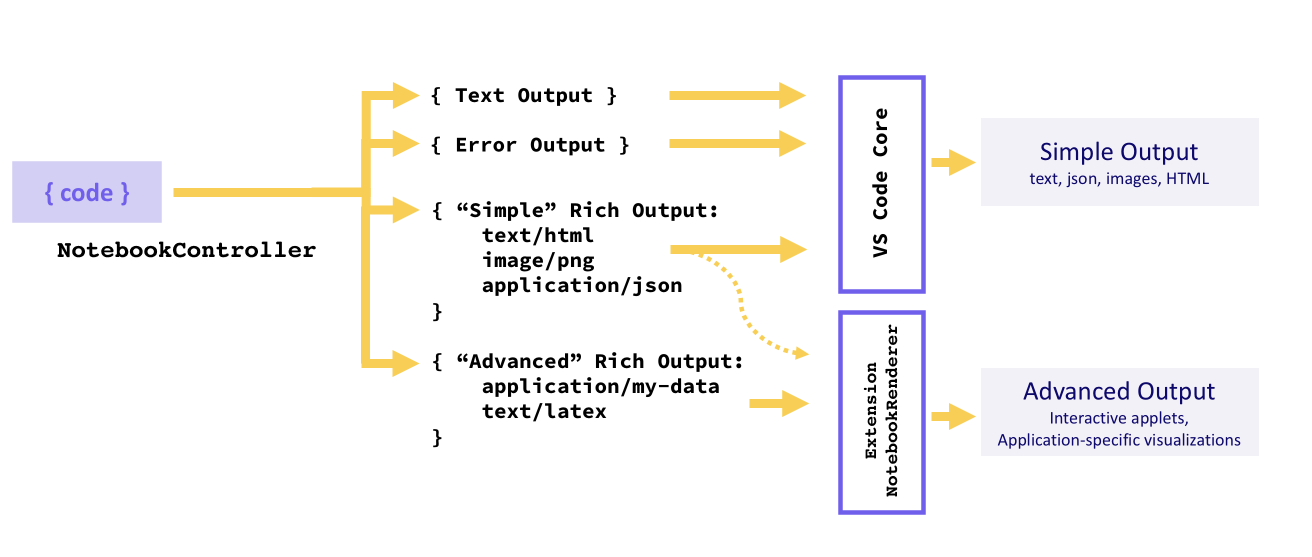
输出类型
输出必须采用以下三种格式之一:文本输出、错误输出或丰富输出。内核可以为单元的单次执行提供多个输出,在这种情况下,它们将显示为列表。
文本输出、错误输出等简单格式或丰富输出的“简单”变体(HTML、Markdown、JSON 等)由 VS Code 核心呈现,而应用程序特定的丰富输出类型由 NotebookRenderer呈现。扩展可以选择渲染“简单”的丰富输出本身,例如向 Markdown 输出添加 LaTeX 支持。
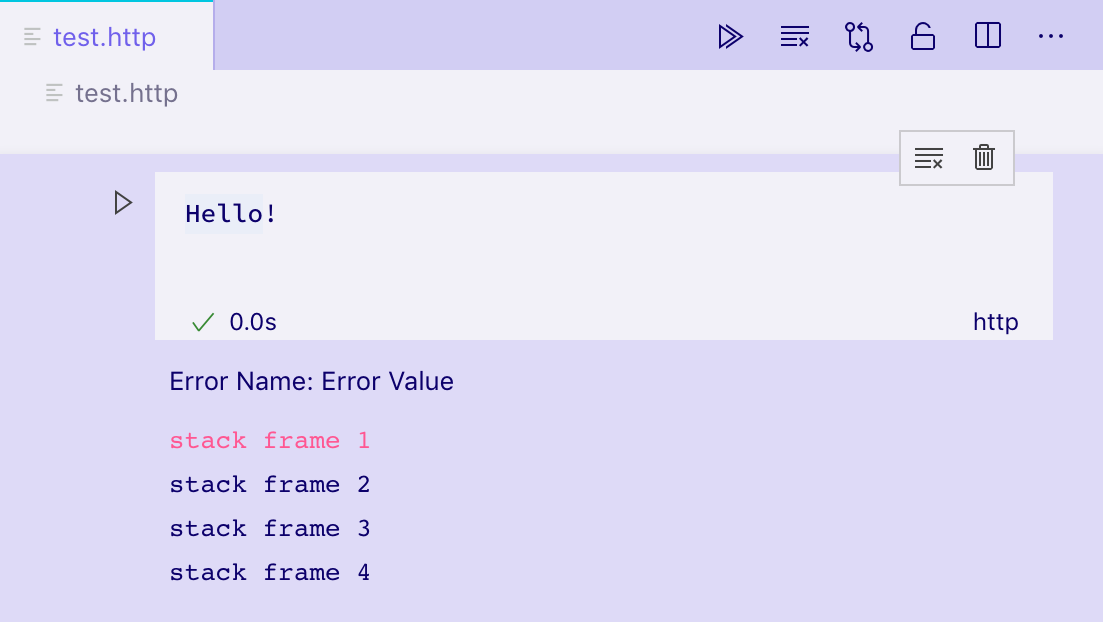
文本输出
文本输出是最简单的输出格式,其工作方式与您可能熟悉的许多 REPL 非常相似。它们仅包含一个text字段,该字段在单元格的输出元素中呈现为纯文本:
vscode.NotebookCellOutputItem.text('This is the output...');

错误输出
错误输出有助于以一致且易于理解的方式显示运行时错误。它们支持标准Error对象。
try {
/* Some code */
} catch (error) {
vscode.NotebookCellOutputItem.error(error);
}
丰富的输出
丰富的输出是显示单元输出的最高级形式。它们允许提供输出数据的许多不同表示形式,由 mimetype 键入。例如,如果一个单元输出代表一个 GitHub 问题,内核可能会生成一个丰富的输出,其data字段上有多个属性:
text/html包含问题的格式化视图的字段。text/x-json包含机器可读视图的字段。application/github-issue可NotebookRenderer用于创建问题的完全交互式视图的字段。
在这种情况下,text/html和text/x-json视图将由 VS Code 本机呈现,但如果没有注册到该 mimetype,application/github-issue则视图将显示错误。NotebookRenderer
execution.replaceOutput([new vscode.NotebookCellOutput([
vscode.NotebookCellOutputItem.text('<b>Hello</b> World', 'text/html'),
vscode.NotebookCellOutputItem.json({ hello: 'world' }),
vscode.NotebookCellOutputItem.json({ custom-data-for-custom-renderer: 'data' }, 'application/custom'),
])]);

默认情况下,VS Code 可以呈现以下 mimetypes:
- 应用程序/javascript
- 文本/html
- 图像/svg+xml
- 文本/降价
- 图片/png
- 图片/jpeg
- 文本/纯文本
VS Code 将在内置编辑器中将这些 mimetype 呈现为代码:
- 文本/x-json
- 文本/x-javascript
- 文本/x-html
- 文本/x-rust
- ... text/x-LANGUAGE_ID 适用于任何其他内置或安装的语言。
此笔记本使用内置编辑器显示一些 Rust 代码:

要呈现替代 mimetype,NotebookRenderer必须为该 mimetype 注册。
笔记本渲染器
笔记本渲染器负责获取特定 mime 类型的输出数据并提供该数据的渲染视图。输出单元共享的渲染器可以维护这些单元之间的全局状态。呈现视图的复杂性范围可以从简单的静态 HTML 到动态的完全交互式小程序。在本节中,我们将探索用于呈现表示 GitHub 问题的输出的各种技术。
您可以使用我们的 Yeoman 生成器中的样板快速开始使用。为此,首先使用以下命令安装 Yeoman 和 VS Code Generators:
npm install -g yo generator-code
然后,运行yo code并选择New Notebook Renderer (TypeScript)。
如果您不使用此模板,您只需确保添加notebookRenderer到keywords扩展程序的 中package.json,并在扩展程序名称或描述中的某处提及其 mimetype,以便用户可以找到您的渲染器。
一个简单的非交互式渲染器
通过贡献contributes.notebookRenderer扩展的package.json. 该渲染器将使用以下ms-vscode.github-issue-notebook/github-issue格式的输入,我们假设某些已安装的控制器能够提供:
{
"activationEvents": ["...."],
"contributes": {
...
"notebookRenderer": [
{
"id": "github-issue-renderer",
"displayName": "GitHub Issue Renderer",
"entrypoint": "./out/renderer.js",
"mimeTypes": [
"ms-vscode.github-issue-notebook/github-issue"
]
}
]
}
}
输出渲染器始终在单个iframeVS Code UI 的其余部分中进行渲染,以确保它们不会意外干扰 VS Code 或导致 VS Code 速度变慢。iframe该贡献涉及一个“入口点”脚本,该脚本在需要渲染任何输出之前加载到笔记本中。您的入口点需要是单个文件,您可以自己编写该文件,也可以使用 Webpack、Rollup 或 Parcel 等捆绑器来创建。
加载后,一旦 VS Code 准备好渲染渲染器,您的入口点脚本应该导出以渲染 UI ActivationFunction。vscode-notebook-renderer例如,这会将所有 GitHub 问题数据以 JSON 形式放入单元格输出中:
import type { ActivationFunction } from 'vscode-notebook-renderer';
export const activate: ActivationFunction = context => ({
renderOutputItem(data, element) {
element.innerText = JSON.stringify(data.json());
}
});
您可以在此处参考完整的 API 定义。如果您使用的是 TypeScript,则可以安装@types/vscode-notebook-renderer并添加vscode-notebook-renderer到types您的数组中tsconfig.json,以使这些类型在您的代码中可用。
要创建更丰富的内容,您可以手动创建 DOM 元素,或使用 Preact 等框架并将其渲染到输出元素中,例如:
import type { ActivationFunction } from 'vscode-notebook-renderer';
import { h, render } from 'preact';
const Issue: FunctionComponent<{ issue: GithubIssue }> = ({ issue }) => (
<div key={issue.number}>
<h2>
{issue.title}
(<a href={`https://github.com/${issue.repo}/issues/${issue.number}`}>#{issue.number}</a>)
</h2>
<img src={issue.user.avatar_url} style={{ float: 'left', width: 32, borderRadius: '50%', marginRight: 20 }} />
<i>@{issue.user.login}</i> Opened: <div style="margin-top: 10px">{issue.body}</div>
</div>
);
const GithubIssues: FunctionComponent<{ issues: GithubIssue[]; }> = ({ issues }) => (
<div>{issues.map(issue => <Issue key={issue.number} issue={issue} />)}</div>
);
export const activate: ActivationFunction = (context) => ({
renderOutputItem(data, element) {
render(<GithubIssues issues={data.json()} />, element);
}
});
在带有数据字段的输出单元上运行此渲染器ms-vscode.github-issue-notebook/github-issue将为我们提供以下静态 HTML 视图:
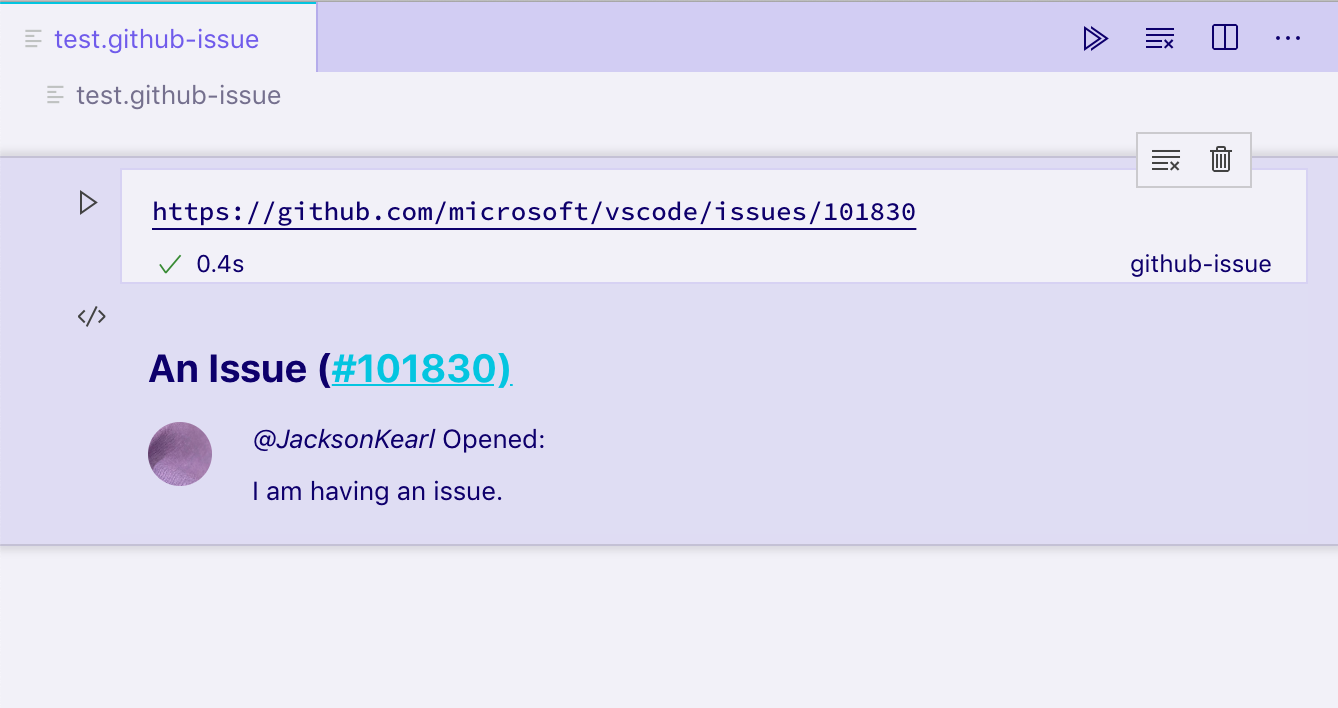
如果您有容器或其他异步进程之外的元素,则可以使用disposeOutputItem来拆除它们。当清除输出、删除单元格以及为现有单元格呈现新输出之前,将触发此事件。例如:
const intervals = new Map();
export const activate: ActivationFunction = (context) => ({
renderOutputItem(data, element) {
render(<GithubIssues issues={data.json()} />, element);
intervals.set(data.mime, setInterval(() => {
if(element.querySelector('h2')) {
element.querySelector('h2')!.style.color = `hsl(${Math.random() * 360}, 100%, 50%)`;
}
}, 1000));
},
disposeOutputItem(id) {
clearInterval(intervals.get(id));
intervals.delete(id);
}
});
请务必记住,笔记本的所有输出都在同一 iframe 中的不同元素中呈现。如果您使用类似 的函数document.querySelector,请确保将其范围限制为您感兴趣的特定输出,以避免与其他输出发生冲突。在此示例中,我们使用它element.querySelector来避免该问题。
交互式笔记本(与控制器通信)
想象一下,我们想要添加在单击渲染输出中的按钮后查看问题评论的功能。假设控制器可以在ms-vscode.github-issue-notebook/github-issue-with-commentsmimetype 下提供带有注释的问题数据,我们可能会尝试预先检索所有注释并按如下方式实现:
const Issue: FunctionComponent<{ issue: GithubIssueWithComments }> = ({ issue }) => {
const [showComments, setShowComments] = useState(false);
return (
<div key={issue.number}>
<h2>
{issue.title}
(<a href={`https://github.com/${issue.repo}/issues/${issue.number}`}>#{issue.number}</a>)
</h2>
<img src={issue.user.avatar_url} style={{ float: 'left', width: 32, borderRadius: '50%', marginRight: 20 }} />
<i>@{issue.user.login}</i> Opened: <div style="margin-top: 10px">{issue.body}</div>
<button onClick={() => setShowComments(true)}>Show Comments</button>
{showComments && issue.comments.map(comment => <div>{comment.text}</div>)}
</div>
);
};
这立即引起了一些注意。其一,我们甚至在单击按钮之前就加载了所有问题的完整评论数据。此外,即使我们只是想显示更多的数据,我们也需要控制器支持完全不同的 mimetype。
相反,控制器可以通过包含预加载脚本来为渲染器提供附加功能,VS Code 也会在 iframe 中加载该脚本。该脚本具有访问全局函数的权限postKernelMessage,onDidReceiveKernelMessage可用于与控制器进行通信。
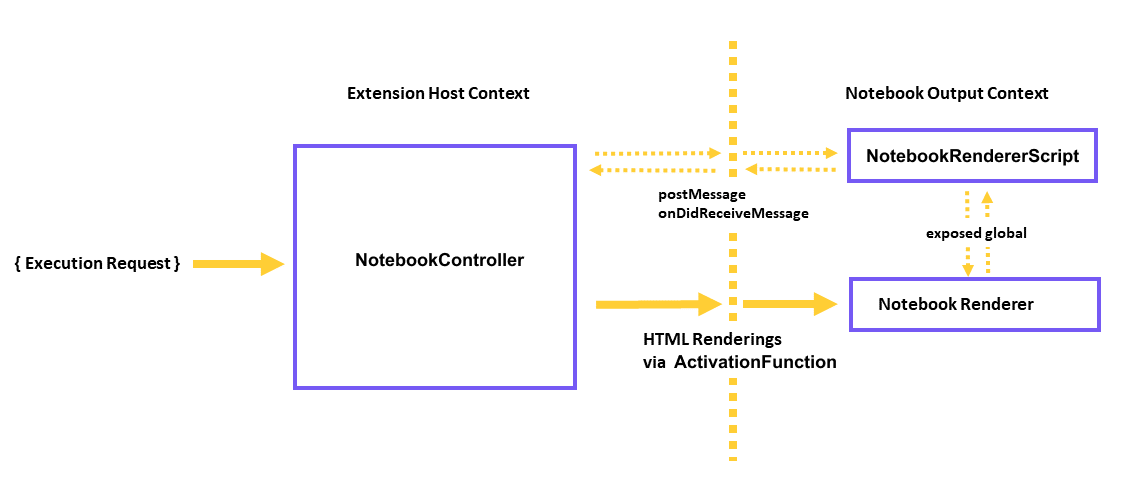
例如,您可以修改控制器rendererScripts以引用一个新文件,在该文件中创建返回到扩展主机的连接,并公开一个全局通信脚本以供渲染器使用。
在你的控制器中:
class Controller {
// ...
readonly rendererScriptId = 'my-renderer-script';
constructor() {
// ...
this._controller.rendererScripts.push(
new vscode.NotebookRendererScript(
vscode.Uri.file(/* path to script */),
rendererScriptId
)
);
}
}
在您package.json指定脚本作为渲染器的依赖项:
{
"activationEvents": ["...."],
"contributes": {
...
"notebookRenderer": [
{
"id": "github-issue-renderer",
"displayName": "GitHub Issue Renderer",
"entrypoint": "./out/renderer.js",
"mimeTypes": [...],
"dependencies": [
"my-renderer-script"
]
}
]
}
}
在脚本文件中,您可以声明与控制器通信的通信函数:
import 'vscode-notebook-renderer/preload';
globalThis.githubIssueCommentProvider = {
loadComments(issueId: string, callback: (comments: GithubComment[]) => void) {
postKernelMessage({ command: 'comments', issueId });
onDidReceiveKernelMessage(event => {
if (event.data.type === 'comments' && event.data.issueId === issueId) {
callback(event.data.comments);
}
});
}
};
然后您可以在渲染器中使用它。您需要确保检查控制器渲染脚本公开的全局是否可用,因为其他开发人员可能会在其他未实现githubIssueCommentProvider. 在这种情况下,如果全局可用,我们将仅显示“加载评论”按钮:
const canLoadComments = globalThis.githubIssueCommentProvider !== undefined;
const Issue: FunctionComponent<{ issue: GithubIssue }> = ({ issue }) => {
const [comments, setComments] = useState([]);
const loadComments = () =>
globalThis.githubIssueCommentProvider.loadComments(issue.id, setComments);
return (
<div key={issue.number}>
<h2>
{issue.title}
(<a href={`https://github.com/${issue.repo}/issues/${issue.number}`}>#{issue.number}</a>)
</h2>
<img src={issue.user.avatar_url} style={{ float: 'left', width: 32, borderRadius: '50%', marginRight: 20 }} />
<i>@{issue.user.login}</i> Opened: <div style="margin-top: 10px">{issue.body}</div>
{canLoadComments && <button onClick={loadComments}>Load Comments</button>}
{comments.map(comment => <div>{comment.text}</div>)}
</div>
);
};
最后,我们要建立与控制器的通信。NotebookController.onDidReceiveMessage当渲染器使用全局函数发布消息时调用该方法postKernelMessage。要实现此方法,请附加到onDidReceiveMessage侦听消息:
class Controller {
// ...
constructor() {
// ...
this._controller.onDidReceiveMessage(event => {
if (event.message.command === 'comments') {
_getCommentsForIssue(event.message.issueId).then(
comments =>
this._controller.postMessage({
type: 'comments',
issueId: event.message.issueId,
comments
}),
event.editor
);
}
});
}
}
交互式笔记本(与分机主机通信)
想象一下,我们想要添加在单独的编辑器中打开输出项的功能。为了实现这一点,渲染器需要能够向扩展主机发送消息,然后扩展主机将启动编辑器。
这在渲染器和控制器是两个单独的扩展的情况下非常有用。
package.json在渲染器扩展的 中指定 as 的值,该requiresMessaging值optional允许渲染器在有权和无权访问扩展主机的两种情况下工作。
{
"activationEvents": ["...."],
"contributes": {
...
"notebookRenderer": [
{
"id": "output-editor-renderer",
"displayName": "Output Editor Renderer",
"entrypoint": "./out/renderer.js",
"mimeTypes": [...],
"requiresMessaging": "optional"
}
]
}
}
可能的值包括requiresMessaging:
always: 需要留言。仅当渲染器是可在扩展主机中运行的扩展的一部分时,才会使用渲染器。optional:当扩展主机可用时,渲染器可以更好地进行消息传递,但不需要安装和运行渲染器。never:渲染器不需要消息传递。
最后两个选项是首选,因为这确保了渲染器扩展到扩展主机可能不一定可用的其他上下文的可移植性。
渲染器脚本文件可以按如下方式设置通信:
import { ActivationFunction } from 'vscode-notebook-renderer';
export const activate: ActivationFunction = (context) => ({
renderOutputItem(data, element) {
// Render the output using the output `data`
....
// The availability of messaging depends on the value in `requiresMessaging`
if (!context.postMessage){
return;
}
// Upon some user action in the output (such as clicking a button),
// send a message to the extension host requesting the launch of the editor.
document.querySelector('#openEditor').addEventListener('click', () => {
context.postMessage({
request: 'showEditor',
data: '<custom data>'
})
});
}
});
然后您可以在扩展主机中使用该消息,如下所示:
const messageChannel = notebooks.createRendererMessaging('output-editor-renderer');
messageChannel.onDidReceiveMessage(e => {
if (e.message.request === 'showEditor') {
// Launch the editor for the output identified by `e.message.data`
}
});
笔记:
- 为了确保您的分机在消息传送之前在分机主机中运行,请添加
onRenderer:<your renderer id>到您的分机功能activationEvents并在分机功能中设置通信activate。 - 并非渲染器扩展发送到扩展主机的所有消息都保证被传递。用户可以在传递来自渲染器的消息之前关闭笔记本。
支持调试
对于某些控制器,例如那些实现编程语言的控制器,可能需要允许调试单元的执行。要添加调试支持,笔记本内核可以通过直接实现调试适配器协议(DAP) 或通过将协议委托和转换给现有笔记本调试器来实现调试适配器(如“vscode-simple-jupyter-”中所做的那样)笔记本样本)。一种更简单的方法是使用现有的未修改的调试扩展并动态转换 DAP 以满足笔记本电脑的需求(如“vscode-nodebook”中所做的那样)。
样品:
- vscode-nodebook:Node.js 笔记本,具有 VS Code 内置 JavaScript 调试器提供的调试支持和一些简单的协议转换
- vscode-simple-jupyter-notebook:Jupyter 笔记本,具有现有 Xeus 调试器提供的调试支持